Orbital and periorbital cellulitis in children (225)

Objectives
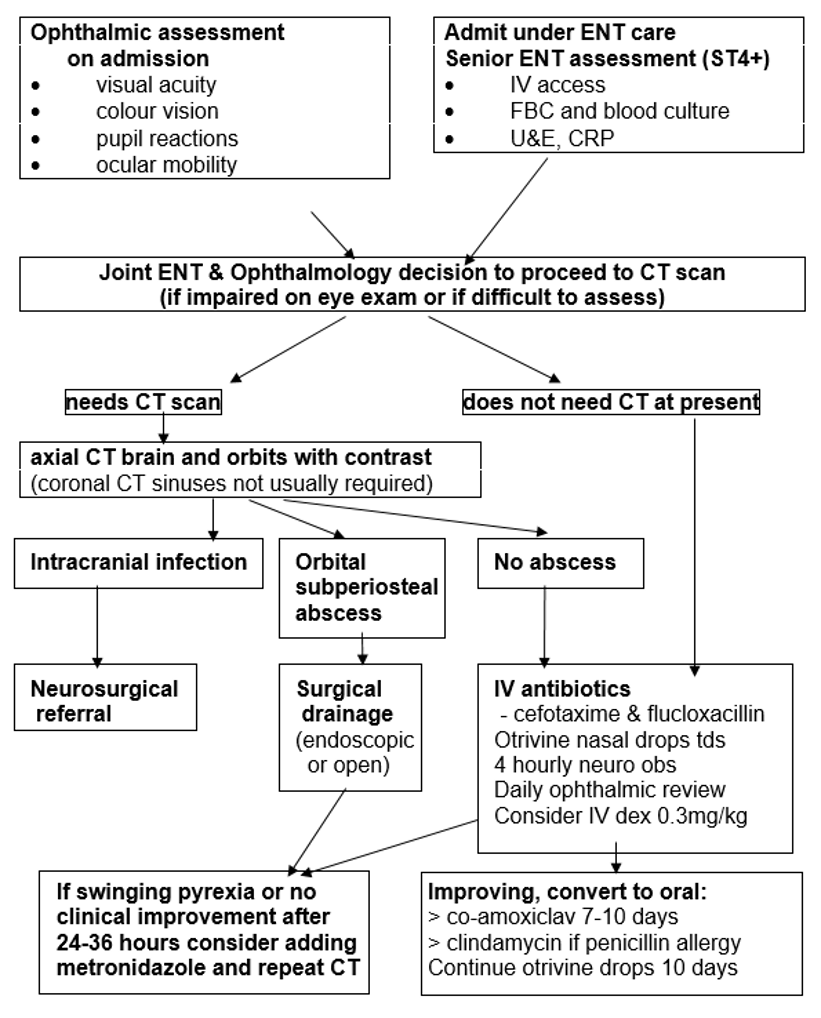
The differentiation between preseptal and deep orbital cellulitis is difficult based on clinical observation and clinical presentation may not always reflect underlying disease severity. Subtle pathology may evolve into severe pathology very quickly. Orbital cellulitis with abscess can lead to permanent blindness within a few hours, and intracranial complications are common and life threatening.
Assessment by an experienced clinician is essential to differentiate the small number of severely affected children who need prompt CT and surgery from the many children with minor infections which settle quickly with medical management. This protocol is based on many years of clinical experience within RHC and it has been shown to be effective in achieving excellent clinical outcomes with very low rates of CT scan compared to other centres [1].
Audience
Medical staff of all grades in paediatric ED, general paediatric medicine, ENT and ophthalmology who might see children with an acutely infected swollen red eye.